Abstract
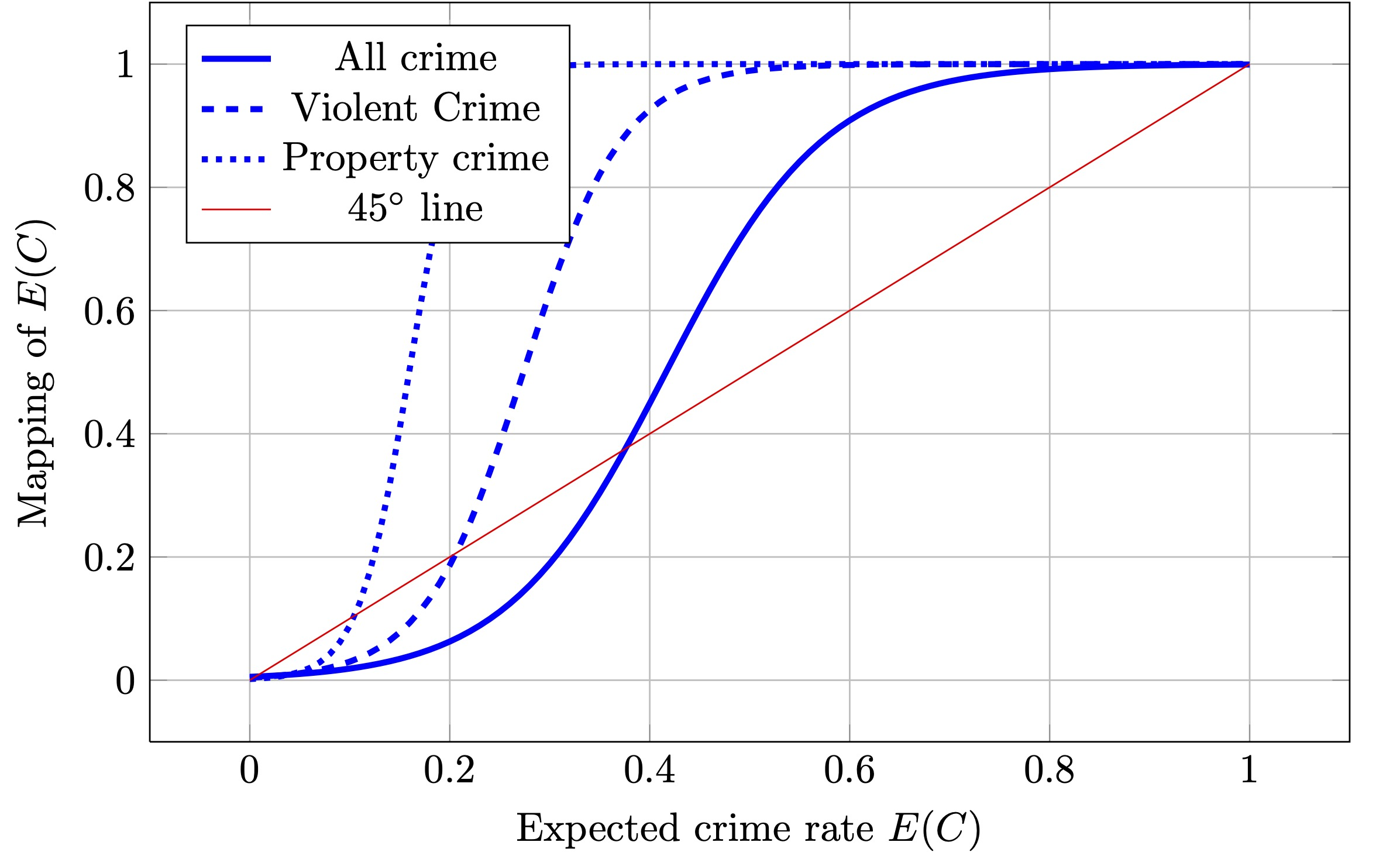
Using data on the age, sex, ethnicity, and criminal involvement of more than 14 million residents of all ages residing in approximately 4,000 Dutch neighborhoods, we test if an individual’s criminal involvement is affected by the proportion of criminals living in his or her residential neighborhood. We develop a binomial discrete choice model for criminal involvement and estimate it on individual data. We control for both the endogeneity that may be related to unobserved neighborhood characteristics and for sorting behavior. We find significant social interaction effects, but our findings do not imply multiple equilibria or large multiplier effects
Illustration
We use a sorting model to map propensity of crime to expected crime propensity yielding multiple equilibria (see below).